ABOUT
STUDY DOMAIN
TIMELINE
The Arctic-Boreal Vulnerability Experiment — ABoVE
Climate change in the Arctic and Boreal region is unfolding faster than anywhere else on Earth, resulting in reduced Arctic sea ice, thawing of permafrost soils, decomposition of long- frozen organic matter, widespread changes to lakes, rivers, coastlines, and alterations of ecosystem structure and function. NASA's Terrestrial Ecology Program is conducting a major field campaign, the Arctic-Boreal Vulnerability Experiment (ABoVE), in Alaska and western Canada, for 8 to 10 years, starting in 2015. ABoVE seeks a better understanding of the vulnerability and resilience of ecosystems and society to this changing environment.
WHAT IS ABoVE?
The Arctic-Boreal Vulnerability Experiment (ABoVE) is a NASA Terrestrial Ecology Program field campaign that will be conducted in Alaska and Western Canada (see Study Domain). ABoVE is a large-scale study of environmental change and its implications for social-ecological systems.
ABoVE’s science objectives are broadly focused on (1) gaining a better understanding of the vulnerability and resilience of Arctic and boreal ecosystems to environmental change in western North America, and (2) providing the scientific basis for informed decision-making to guide societal responses at local to international levels. Research for ABoVE will link field-based, process-level studies with geospatial data products derived from airborne and satellite sensors, providing a foundation for improving the analysis, and modeling capabilities needed to understand and predict ecosystem responses and societal implications.
The planning for ABoVE started in 2009 with a scoping study. Throughout 2013, the science definition team wrote a concise experiment plan that was completed 2014. The first ABoVE call for proposals appeared in ROSES 2014 (see Timeline).
WHY DO WE NEED TO STUDY THE ARCTIC AND BOREAL REGION?
Climate change in the Arctic and Boreal Region (ABR) is unfolding faster than anywhere else on Earth, resulting in reduced volume and area of sea ice in the Arctic Ocean during summer, warming and thawing of permafrost, increases in the frequency and severity of climate-driven disturbances, and widespread changes to surface water extent, soil moisture, and vegetation structure and function. Environmental and climate change in the ABR is increasingly affecting society both locally and globally. Changes to forests from insects and fires, erosion of Arctic coastlines, and altered wildlife habitats that support subsistence opportunities may affect residents of the ABR both positively and negatively. The ABR also contains a globally significant amount of carbon in both the soils and vegetation, and it is unknown how much of this sequestered carbon will be released to the atmosphere as permafrost thaws and forests burn, potentially further accelerating global climate change.
WHY NASA?
Research addressing the ABoVE research objectives benefits from the unique capabilities provided by remote sensing data. Data products from new and existing satellite and airborne remote sensing systems allow for the study of seasonal and inter-annual variability over large geographic regions. At landscape to regional scales, these data products will be critical to the spatial and temporal scaling of observations made from field studies. Conversely, field observations play a vital role in the refinement and validation of remotely sensed data products.
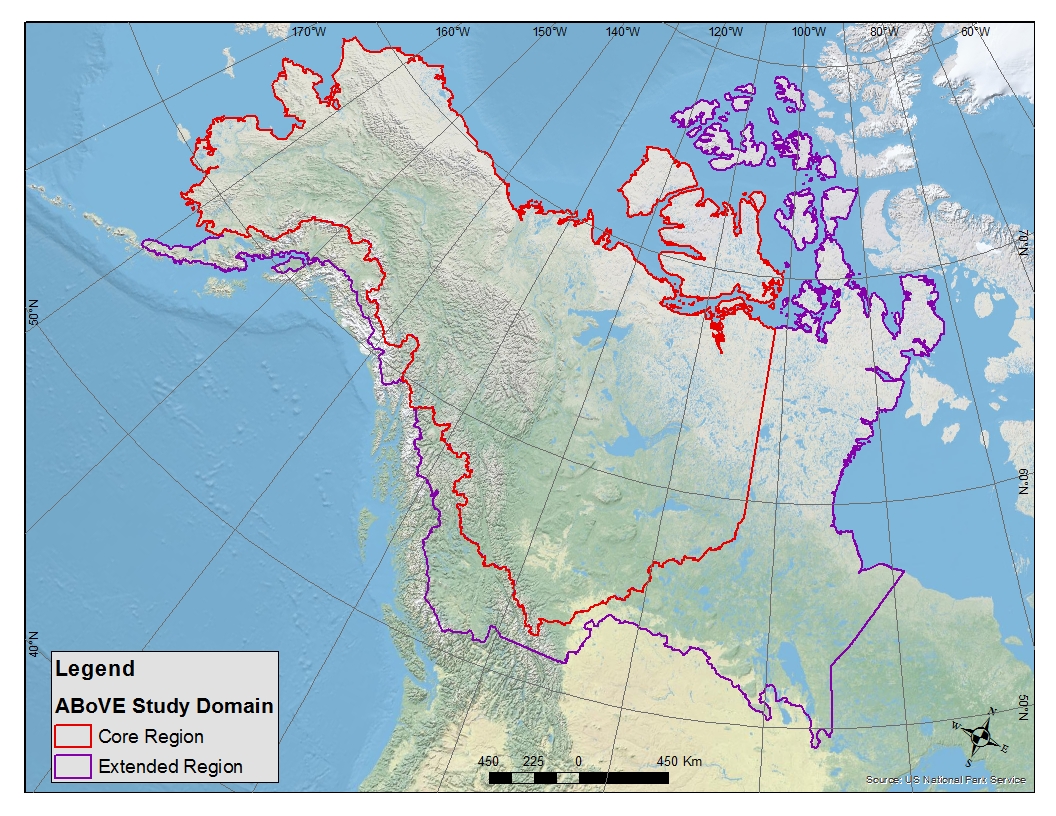
Study Domain
Research and analysis activities for ABoVE will be carried out in study sites located across western Canada and Alaska. Studies will be carried out over a range of spatial scales, including within different terrestrial ecoregions, within primary and secondary research areas, within discrete landscape units (such as a watershed or disturbance event), and within plots (at a scale of 10 m to 1 km). The exact geographic boundaries and location of study sites will be determined in the more detailed planning activities to follow, and will be influenced by collaborating programs and projects.
Download the ESRI Shapefile and/or TIFF of the ABoVE Study Domain, or access on the web as an item in ArcGIS Online where it can be viewed, downloaded locally, or added to a map as a web feature service.